DOWNLOAD SLIDE HERE
Exam Answers v3.x and v4.0
Options with "*" are correct answer
time exceeded
redirect
* destination unreachable
source quench
parameter problem
echo reply
2 Which two are true regarding the debug commands? (Choose two.)
Debug commands may be issued from the user EXEC prompt.
* The command undebug all will turn off all debug operations.
By default, the router sends the debug output and messages to the telnet session.
* The high processor overhead incurred using debug may disrupt normal router operation.
The debug all command provides a summary view of router activity and can be used frequently for troubleshooting.
The show debugging command will display current events such as traffic on an interface and error messages generated by nodes on the network.
3 Which of the following commands can be used to statically configure default routes? (Choose two.)
ip static-route
* ip route
ip network-route
* ip default-network
ip default-static
4 At which OSI layer does the routing of email packets from the source network to the destination network occur?
application
session
transport
* network
5 When issuing the show interfaces serial1 command, a network administrator receives the output shown in the graphic. What are the possible causes of an increase in the number of input errors? (Choose three.)
There could be Layer 3 addressing problems.
* There could be a problem with faulty telephone equipment.
* The router hardware could be defective.
There is an incorrectly configured encapsulation on the interface.
* There could be a problem with the cabling.
6 Which two are true regarding the output shown in the graphic? (Choose two.)
Network 192.168.44.0 is 610 routers away from the source router.
* A packet destined for host 192.168.80.24 will be forwarded out the Serial0 interface.
The subnet mask for the networks is 255.255.255.240.
* The router is receiving IGRP updates through its serial interface.
This router is using three different routing protocols.
7 The show interfaces command provides line and protocol status information. Which of the following conditions would never occur in the output of this command?
serial1 is up, line protocol is up
serial1 is up, line protocol is down
serial1 is down, line protocol is down
* serial1 is down, line protocol is up
serial1 is administratively down, line protocol is down
8 After issuing the command traceroute 192.168.4.2 from Router A, the following information is returned.
Tracing the route to Router_D (192.168.4.2)
1 Router_B (192.168.2.2) 16 msec 16 msec 16 msec
2 * * *
3 * * *
What can be concluded about the network shown in the graphic based on the output given?
Network 192.168.5.0 is missing from the routing table on Router A.
* There is a problem with the connection between Router B and Router C.
Router C is not running CDP.
Some of the routers are non-Cisco devices.
Router B was not able to return ICMP TEMs to Router A.
9 During the lookup process when forwarding a packet, a router checks its routing table for the best path to the destination. If a route has an administrative distance of 0, what does this indicate to the router?
The packet should be discarded.
The destination is unreachable.
* The destination is a directly connected network.
The source of the update for that route is unreliable.
10 Which of the following would be the default administrative distance of a static IP route that references the IP address of the next hop?
0
* 1
5
20
11 Which items would be displayed when the show ip protocol command is executed? (Choose three.)
* sources of routing updates
* networks being advertised
routing protocol up or down
configured routed protocols
Layer 2 status of the interface
* update timer values
12 A network administrator suspects that a network is not being included in the routing updates. Which command will provide information on when the next update is due and which networks are advertised in the update?
Router# show interfaces
Router# show controllers serial
* Router# show ip protocols
Router# show ip route
Router# show running-config
13 Which of the following lines from the show interfaces output would indicate a Layer 2 problem?
Serial1 is up, line protocol is up.
* Serial1 is up, line protocol is down.
Serial1 is down, line protocol is down.
Serial1 is administratively down, line protocol is down.
14 After issuing the show interfaces command, a technician notices the line "Serial1 is down, line protocol is down" in the output. Which of the following are possible reasons for this message output? (Choose three.)
There is a mismatch in the encapsulation type on both ends of the link.
* A Layer 1 issue exists.
* An interface problem exists.
The clockrate was not set during configuration.
* There is no usable media for the protocol.
Keepalive messages are not being sent.
15 Refer to the network graphic. A packet needs to travel from Router F to Router A. Which path would be selected by the RIP routing protocol if the default metrics are used?
F, G, E, D, B, A
F, E, D, C, A
* F, E, D, A
F, E, D, B, A
16 Which command will verify the functionality of all seven layers of the OSI model on a network host?
ping
* telnet
tracert
debug
17 Why does a router build a routing table? (Choose two.)
* to list available routes for forwarding data
to map local Layer 2 addresses to the remote Layer 3 destination address
to dynamically send periodic updates regarding the router's status
to prevent routing loops when redundant links are added to the network
* to select the best path to a destination
18 Which of the following are advantages of using a static route? (Choose three.)
* secure operation
highly adaptable
low maintenance configuration
* low processor overhead
* precise control of path selection
19 After issuing the show interfaces serial1 command, an administrator notices an increasing number of carrier transitions. What are the possible causes for this increase? (Choose two.)
There is an incorrect encapsulation configured on the interface.
* There could be an interruption in the line by the service provider.
* There is a faulty switch or CSU/DSU.
There is noise on the serial line.
20 Which command will display routing table information about all known networks and subnetworks?
Router# show ip interfaces
Router# show ip connections
* Router# show ip route
Router# show ip networks
21 Consider the RIP network shown in the diagram. Which entries would be listed in the routing table of Router A?
R 192.168.5.2[120/1] via 192.168.15.0, 00:00:09, Serial0
R 192.168.15.0[120/1] via 192.168.5.2, 00:00:13, Serial1
* R 192.168.15.0[120/1] via 192.168.5.1, 00:00:13, Serial0
R 192.158.5.1 [120/1] via 192.168.5.2 00:00:29, Serial1
R 192.168.15.0 [120/1] via 192.168.5.2, 00:00:29, Serial1
R 192.158.5.1 [120/1] via 192.168.5.2 00:00:18, Serial0
R 192.168.15.2 [120/1] via 192.168.5.2, 00:00:18, Serial
22 The network administrator shown in the graphic can ping the E0 interface of the HAR router, but the telnet intranet.xyz.com command issued from her workstation fails to open a session with the intranet.xyz.com server. Which of the following could cause this problem? (Choose two.)
* upper-layer application problems
* domain name system problems
IP debugging problems
IP routing problems
ICMP connectivity problems
23 Refer to the network and routing table entries shown in the graphic. What will happen when a packet destined for network 192.66.7.0 is received by Router A?
It will be forwarded through interface S1.
It will be forwarded to the default route.
It will be directed toward the Internet.
* It will be discarded.
V4.0
Options with highlight colours are correct answer
1. What two actions will the EIGRP DUAL FSM take if a link to a network goes down? (Choose two.)
• put the route into passive mode
• query neighbors for a new route
• search routing table for a feasible successor
• run the SPF algorithm to find a new successor
• search topology table for a feasible successor
2. Host 192.168.1.66 in the network illustrated is unable to ping host 192.168.1.130. How must EIGRP be configured to enable connectivity between the two hosts? (Choose two.) 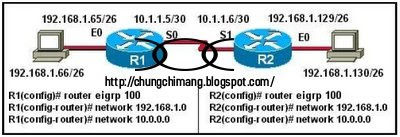
• R1(config-router)# network 192.168.1.128
• R1(config-router)# auto-summary
• R1(config-router)# no auto-summary
• R2(config-router)# no auto-summary
• R2(config-router)# auto-summary
• R2(config-router)# network 192.168.1.64
3. Refer to the exhibit. The company is using EIGRP with an autonomous system number of 10. Pings between hosts on networks that are connected to router A and those that are connected to router B are successful. However, users on the 192.168.3.0 network are unable to reach users on the 192.168.1.32 network. What is the most likely cause of this problem? 
• IP classless is enabled and is causing the packet to drop.
• The command network 192.168.1.32 was not issued on router C.
• The routers are not configured in the same EIGRP routing domain.
• Automatic summarization of the networks is causing the subnetted routes to be dropped.
4. What information is maintained in the EIGRP topology database for a destination route? (Choose three.)
• the routing protocol
• the feasible distance of the route
• the highest cost of the route
• the SRTT value for the route
• the route cost as advertised by the neighboring router
• the physical address of the gateway interface
5. On a router running EIGRP, what database would maintain a list of feasible successors?
• routing table
• neighbor table
• topology table
• adjacency table
6. Refer to the exhibit. What is indicated by the P at the beginning of the topology entry? 
• the route is in a stable state
• the route is a preferred route
• DUAL is searching for a better route to this destination
• the exit interface is in passive mode and EIGRP advertisements are blocked
7. In the command router eigrp 20, what is the purpose of the number 20?
• specifies the administrative distance for all EIGRP routes
• identifies the autonomous system number this EIGRP process will advertise
• determines what metric is added to all advertised routes
• indicates the number of addresses in the EIGRP routing domain
8. Refer to the exhibit. In the topology table, what do the numbers 3011840 and 3128695 represent? 
• the route metric that is applied to those EIGRP routes for this router
• the trustworthiness of the routing information source
• the composite of the hop count and bandwidth to that destination network
• the total metric for that network as advertised by the EIGRP neighbor
9. Which two statements describe characteristics of EIGRP? (Choose two.)
• EIGRP is a distance vector routing protocol.
• EIGRP supports classless routing and VLSM.
• EIGRP is classified as a link-state routing protocol.
• EIGRP uses TCP for reliable delivery of EIGRP update packets.
• With EIGRP, loop-free paths are achieved through the use of hold-down timers.
• EIGRP sends a periodic update every 30 minutes.
10. Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.0.0/28 goes down. What type of packet does Router2 immediately send to Router1 and Router3? 
• a query for network 192.168.0.0/28
• an acknowledgment packet to 224.0.0.9
• an update packet that is sent to 255.255.255.255
• a packet that contains the new routing table for R2
• unicast update packets to 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1
11. Refer to the exhibit. Network 192.168.0.0/28 goes down. What type of packet does Router2 immediately send to Router1 and Router3?
• a query for network 192.168.0.0/28
• an acknowledgment packet to 224.0.0.9
• an update packet that is sent to 255.255.255.255
• a packet that contains the new routing table for R2
• unicast update packets to 192.168.1.1 and 192.168.2.1
12. What administrative distance would a router assign to a default route in EIGRP that is learned from a source external to the autonomous system?
• 1
• 5
• 70
• 90
• 170
• 190
13. In which of the following tables does the EIGRP DUAL algorithm store the primary route to a destination? (Choose two.)
• routing
• topology
• neighbor
• path
• shortest path
14. Which of the following types of routes will be denoted by EX in EIGRP routing table entries? (Choose two.)
• routes learned from other routing protocols
• routes learned from any non-adjacent EIGRP routers
• any route with a hop count metric higher than 224
• EIGRP routes that originate in different autonomous systems
• all passive routes in the routing table
15. Which term defines a collection of networks under the administrative control of a single entity that presents a common routing policy to the Internet?
• autonomous system
• contiguous networks
• process ID
• BGP
16. Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is the only routing protocol enabled on this network. No static routes are configured on this router. What can be concluded about network 198.18.1.0/24 from the exhibited output?
• A route to network 198.18.1.0/24 is not listed in the routing table.
• Packets that are destined for 198.18.1.0/24 will be forwarded to 198.18.10.6.
• EIGRP will perform equal cost load balancing across two paths when forwarding packets to 198.18
17. The router with interface 172.16.3.2 is a successor for network 198.18.1.0/24. Refer to the exhibit. All interfaces have been configured with the bandwidths that are shown in the example. Assuming that all routers are using a default configuration of EIGRP as their routing protocol, what packets take from the 172.16.1.0/16 network to the 192.168.200.0/24 network? 
• A,B,E
• A,C,E
• A,D,E
• Packets will load balance across the A,B,E and A,C,E paths.
• Packets will load balance across the A,B,E and A,D,E paths.
• Packets will load balance across the A,C,E and A,D,E paths.
18. By default, which two metrics are used by EIGRP to determine the best path between networks?
• MTU
• load
• delay
• bandwidth
• reliability
19. Which of the following statements describes the bounded updates used by EIGRP?
Bounded updates are sent to all routers within an autonomous system.
• Partial updates are sent only to routers that need the information.
The updates are sent to all routers in the routing table.
Updates are bounded by the routers in the topology table.
20. The show ip eigrp topology command output on a router displays a successor route and a feasible successor route to network 192.168.1.0/24. In order to reduce processor utilization, what does EIGRP do when the primary route to this network fails?
• The router sends query packets to all EIGRP neighbors for a better route to network 192.168.1.0/24.
• The DUAL FSM immediately recomputes the algorithm to calculate the next backup route.
• Packets that are destined for network 192.168.1.0/24 are sent out the default gateway instead.
• The backup route to network 192.168.1.0/24 is installed in the routing table.
21. Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output of show ip eigrp neighbors, what are two possible problems with adjacencies between Router1 and Router2? (Choose two.) 
• The routers are configured with different EIGRP process IDs.
• Automatic summarization was disabled.
• The hello timer for R1 was altered.
• The serial interfaces for both routers are in different networks.
• No feasible successors were found.
22. Refer to the exhibit. This is the debug output from 2 directly connected EIGRP routers. They are not forming an adjacency. What is the cause? 
• one router is a non-cisco router
• they have different autonomous-system numbers
• they are using difference sequence numbers
• they are sending incorrect hello types
23. Refer to the exhibit. Which command will advertise the 192.168.1.64/30 network but not the 192.168.1.32 network on router A? 
• network 192.168.1.0
• network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
• network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.3
• network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.7
• network 192.168.1.64 0.0.0.255





No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank for your comments!!!